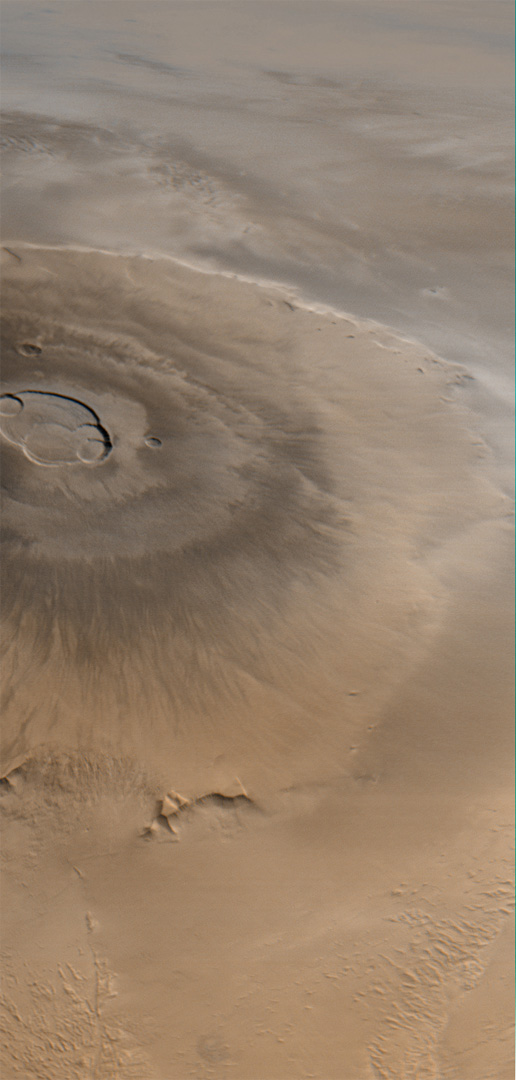
Scientists have grouped volcanoes into three general types based largely on their shape, and on the type of materials they erupt. These are: shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and cinder cone volcanoes.
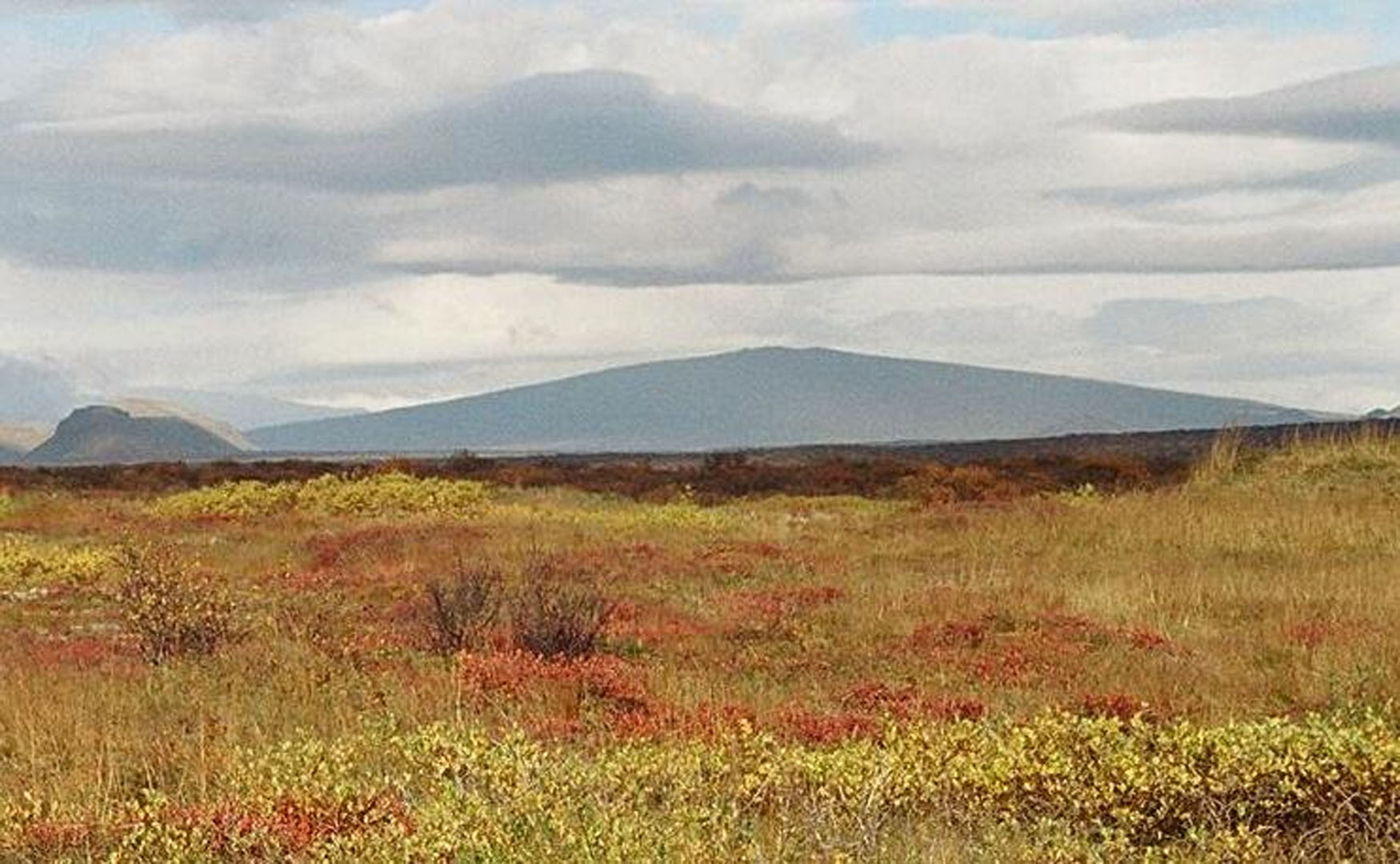
Shield volcanoes are roughly oval shaped and have a broad base with gently sloping sides that have angles up to about 10°. Shield volcanoes are formed by repeated mafic lava flows that build up over time around a central vent. Shield volcanoes are composed primarily of basaltic rock since they are formed by mafic lava flows.
Shield volcanoes are among the largest volcanoes in the world since they are built up slowly over a fairly long period of time. The volcanoes of the Hawaiian Islands, the Galapagos Islands, and Iceland are all shield volcanoes. Mauna Loa, a shield volcano on the Big Island of Hawaii, is actually the world’s largest shield volcano with a diameter of over 80 kilometers (50 miles) at its base.
- Click here to see the world distribution of all volcanoes.
- Click here to see the world distribution of shield volcanoes only.
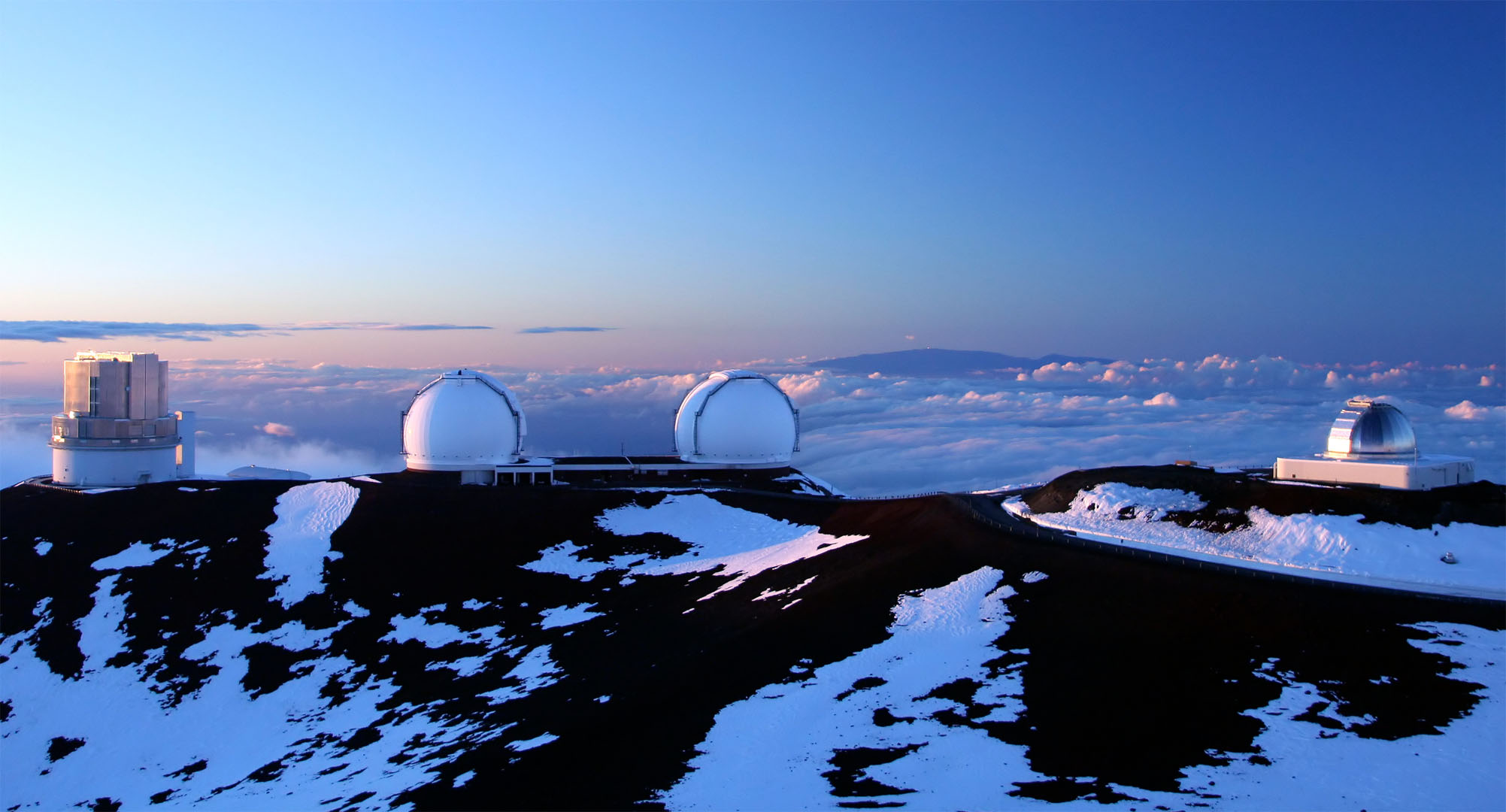
Measuring Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea on the Big Island of Hawaii is the tallest volcano in the Hawaiian Islands chain of volcanoes.
- Click here to view Mauna Kea.
- Click here to add in a terrain profile starting on the flanks of Mauna Kea.
- What is the elevation of Mauna Kea at this point?
Mauna Kea has an elevation of 3,501 m (11,490 ft) at this point.
- Slowly shift your screen view until you find the maximum elevation for Mauna Kea. (Hint: Click here if you have trouble finding the maximum elevation.)
- What is the maximum elevation of Mauna Kea?
The maximum elevation for Mauna Kea using our terrain profile is 4,194 m (13,760 ft). (Note the official height for Mauna Kea is 4,205 m / 13,790 ft.)
Mauna Kea, however, extends well below the surface of the Pacific Ocean. The part that we see above water represents less than half of the actual size of Mauna Kea.
- Zoom out in your view until you see a clear terrain profile of Mauna Kea that also shows its maximum depth underwater. (Hint: Click here if you need help with this.)
- How much of Mauna Kea is underwater at this point?
Mauna Kea extends for another 5,591 m (18,340 ft) underwater at this point. - What is the actual height of Mauna Kea as measured from the ocean floor?
Our current terrain profile shows a total height for Mauna Kea of 9,683 m (5,591 m + 4,092 m) or 31,770 ft. (Note that our height above ground has changed slightly from our answer in question 2 because of a slight loss in resolution/precision the further above the Earth’s surface that we get. Using our slightly more accurate value from question 2 would give a total height for Mauna Kea of 9,785 m (32,100 ft).
Mt. Everest, with an elevation of 8,848 m (29,029 ft) is often called the highest mountain in the world.
- Which mountain is really the highest mountain in the world, Mt. Everest or Mauna Kea, and by how much?
Mauna Kea is really the highest mountain in the world when measured from its base. Its height exceeds that of Everest by 835 m / 2,741 ft (using 9,683 m as the total height) or by 937 m / 3,071 ft (using the slightly more accurate 9,785 m as the total height).